Overview
Materials development is a fundamental activity at SPINTEC, a determining factor for the success of our research projects. The Materials Growth team assists and participates on the development and characterization of new materials and stacks for the different research projects. Sputtering and molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) are our two main deposition techniques. The team also maintains our tools at the best operational order and upgrades them to keep them at the state of the art.
Most of our research teams depend on our sputtering facilities, capable of depositing a wide range of metals, rare earths and oxides in an industrially friendly fashion. We currently have two tools in operation (ACTEMIUM and PLASSYS) and a third one under construction in-house (Convergence).
Techniques and equipments
ACTEMIUM – Sputtering

ACTEMIUM is our main tool with 12 sputtering sources under very high vacuum (10-8 mbar) capable of DC and RF excitation for conducting and isolating targets. In this tool, a separate treatment chamber allows us to plasma clean the substrates prior to deposition or to oxidize films by exposing them to oxygen with a possible plasma assistance. This tool allows us to deposit extremely complex stacks with up to dozens of individual films and thicknesses down to 0.1 nm. Common stacks include MgO insulating barriers for magnetic tunneling junctions (MTJ), Pt/Co multilayers with perpendicular anisotropy, and synthetic antiferromagnetic stacks with RKKY coupling.
Convergence – Sputtering
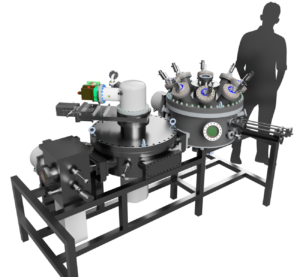
Convergence is a new UHV sputtering tool under construction in-house that will be dedicated to the development of new materials, with shorter campaigns than with our other tools. The design consists on three chambers: load-lock, distribution and deposition chamber, the latter with 8 convergent sources. Simplicity and modularity are the main features of this machine, that will be able to evolve over time with ports reserved for two additional chambers and an exchangeable sample holder.
Annealing

Annealing is a fundamental step in most of our stacks. We anneal routinely to pin a ferromagnetic layer in a given direction with an adjacent antiferromagnetic layer or to crystallize amorphous films. We are equipped with a MATr 2000 200mm oven capable of applying a magnetic field of up to 2 T, a rapid thermal annealing 100 mm oven, and a small sample oven with up to 0.2 T field.
Current in plane tunneling
Magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJ) are basic building blocks of many of our stacks. After deposition, a quick feedback on their properties is key for a fast development cycle. The CAPRES CIPT tool allow us to measure the tunneling magneto resistance (TMR) without the need of time-consuming nanofabrication procedures.
Molecular Beam Epitaxy
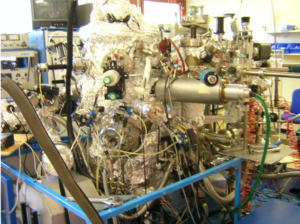
We use a custom-made cluster for the growth of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDC) and topological insulators (TI). The UHV cluster is equipped with 2 Kundsen cells, 11 crucibles for e-beam evaporation, 4 sputtering sources and a sample holder capable of heating up to 1300 K. RHEED characterization is possible during growth. With this tool we are able to create 2D systems at the interface between two films.
The team
Recent news
- Monolayer control of spin-charge conversion in van der Waals Heterostructures (September 16th, 2025)
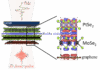
2D materials and van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures are promising candidates to build efficient THz spintronic emitters. Here, we demonstrate the drastic modification of THz spintronic emission by inserting a single layer of MoSe2 in ... - Modulating TeraHertz emission using 2D materials and ferroelectricity (September 08th, 2025)
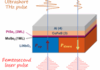
The modulation of THz spintronic emitters represents a real challenge nowadays. Here, we consider a THz emitter made of 2D materials grown by molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) on large area and transferred on LiNbO3. The ... - Synthetic antiferromagnetic skyrmions moving at record speeds (June 24th, 2024)
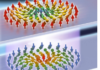
Magnetic skyrmions are magnetic nanobubbles which are envisioned as bits of informations in our computers. A team from the Spintec laboratory in Grenoble has demonstrated that they can be moved by electric current at ... - Recruiting a 24 month Fixed Term R&D Engineer on developing magnetic materials and stacks for Spintronics (March 13th, 2023)

Context: SPINTEC opens a R&D Engineer position for developing magnetic multilayer stacks on a new fully automated ultra-high vacuum sputtering tool for 100 mm wafers, developed in-house. The work will be carried out within the “Materials” ... - PEPR SPIN – Priority Programs and Equipment for Exploratory Research (July 29th, 2022)

France is investing more than 38M€ in Spintronics thanks to the PEPR-SPIN exploratory program! SPIN is among the 13 new exploratory programs winners of the second wave of calls for projects Priority Programs and ...













